-
CCPA: California Consumer Privacy Act
- A privacy law in California that grants California consumers certain rights regarding their personal information. It imposes regulations on businesses to safeguard and provide transparency about the collection and use of consumer data.
-
SPD: Security Policy Document
- A document that outlines an organization's security policies, defining rules, procedures, and guidelines to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of its information assets.
-
IGRC: Integrated Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance
- An approach that integrates governance, risk management, and compliance activities within an organization to streamline processes, reduce redundancy, and enhance overall effectiveness.
-
CSMF: Cybersecurity Management Framework
- A structured approach or framework used by organizations to manage and improve their cybersecurity posture. It typically includes policies, processes, and technologies to protect against cyber threats.
-
MEGCSMM: Model for the Evaluation of Government Cybersecurity Management Maturity
- A model used for assessing and evaluating the maturity of cybersecurity management practices within government organizations.
-
ERM: Enterprise Risk Management
- A holistic approach to identifying, assessing, and managing risks across an entire organization. It includes processes and strategies to address various risks, including cybersecurity risks.
-
GRC: Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance
- A framework that integrates these three components to ensure an organization operates efficiently, manages risks effectively, and complies with applicable regulations and standards.
-
HITECH: Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act
- Legislation in the United States that promotes the adoption and meaningful use of health information technology. It includes provisions for the security and privacy of electronic health records.
-
GISES: Global Information Security and Ethical Standards
- A set of standards and guidelines related to information security and ethical practices on a global scale.
-
SaaS: Software as a Service
- A cloud computing model where software applications are provided over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access the software through a web browser without the need for local installation.
-
BYOD: Bring Your Own Device
- A policy that allows employees to use their personal devices, such as smartphones or laptops, to access company networks and resources. It requires security measures to mitigate associated risks.
- Definition: Internet hacking refers to the unauthorized access, manipulation, or disruption of computer systems or networks connected to the internet.
- Objective: Hackers may seek to exploit vulnerabilities for various reasons, including stealing sensitive information, causing disruptions, or gaining control over systems for malicious purposes.
- Methods: Techniques such as exploiting software vulnerabilities, social engineering, phishing, and malware deployment are commonly used in internet hacking.
- Definition: Digital laws, also known as cyber laws or internet laws, refer to legal regulations that govern online activities, transactions, and interactions.
- Purpose: Digital laws aim to address issues such as online privacy, data protection, intellectual property rights, cybercrime, and electronic commerce.
- Examples: Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), and various national laws that define legal frameworks for the digital realm.
- Definition: Cybercrime encompasses criminal activities carried out through the use of computer systems or the internet. It includes offenses such as hacking, identity theft, online fraud, and distribution of malicious software.
- Categories: Cybercrime can be categorized into various types, including financial crimes, identity theft, cyber espionage, and attacks on critical infrastructure.
- Prevention: Prevention strategies involve implementing robust cybersecurity measures, raising awareness, and enforcing digital laws.
- Unfortunately, I don't have a specific model with that exact name in my training data. However, a sustainable partnership development model generally involves establishing and maintaining partnerships that are mutually beneficial, environmentally friendly, and socially responsible. It may include stages such as identification of partners, collaboration, and ongoing evaluation.
- A holistic risk model for cloud computing should consider known and unknown factors. It typically involves:
- Identification: Identifying known risks such as data breaches, service outages, and compliance issues.
- Assessment: Evaluating the impact and likelihood of known risks while considering potential unknown risks associated with emerging technologies or evolving threats.
- Mitigation: Implementing measures to address both known and potential unknown risks, including robust security controls, encryption, and regular monitoring.
- Unfortunately, I don't have specific information on an "Integrated Resilience Management Model" in my training data. However, such a model would likely involve strategies for building organizational resilience by integrating risk management, business continuity, and incident response.
- The business continuity planning process typically involves the following stages:
- Initiation: Establishing the need for business continuity planning.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and assessing potential risks and vulnerabilities.
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Evaluating the impact of disruptions on business processes.
- Strategy Development: Developing strategies to mitigate risks and ensure continuity.
- Plan Development: Creating detailed business continuity plans.
- Training and Awareness: Training personnel and raising awareness about the plans.
- Testing and Exercising: Conducting drills and exercises to ensure the effectiveness of plans.
- Maintenance and Review: Regularly reviewing and updating plans to reflect changes in the business environment.
- Audit and Continuous Improvement: Conducting audits and incorporating lessons learned for continuous improvement.
-
Incident Response Analysis:
- Involves investigating and responding to cybersecurity incidents, including data breaches or system compromises.
-
Vulnerability Analysis:
- Identifies and assesses vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications to prevent potential exploitation.
-
Threat Intelligence Analysis:
- Involves collecting and analyzing information about potential cyber threats to understand the tactics, techniques, and procedures of adversaries.
-
Risk Analysis:
- Evaluates the potential impact and likelihood of cybersecurity risks to make informed decisions on risk mitigation strategies.
-
Forensic Analysis:
- Examines digital evidence to uncover the root cause of security incidents and gather information for legal purposes.
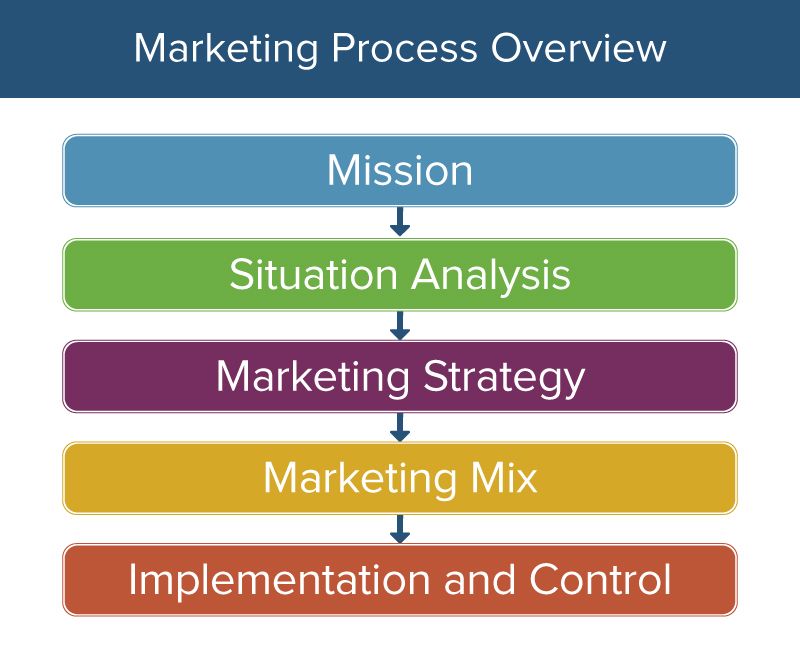
- Market Analysis: Understand the market, including customer needs, competitors, and trends.
- Target Market: Identify specific segments to target based on analysis.
- Value Proposition: Clearly communicate the unique value your product or service offers.
- Marketing Mix (4 Ps):
- Product: Develop a quality product.
- Price: Set a competitive and profitable price.
- Place: Choose the right distribution channels.
- Promotion: Use effective promotional strategies.
-
Risk Management Principles:
- Integration: Embed risk management into organizational processes.
- Customization: Tailor the approach based on context.
- Inclusiveness: Involve stakeholders in the risk management process.
-
Risk Management Framework:
- Identification: Identify risks relevant to organizational objectives.
- Assessment: Evaluate the potential impact and likelihood of identified risks.
- Treatment: Develop and implement strategies to manage or mitigate risks.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously monitor and review the risk management process.
-
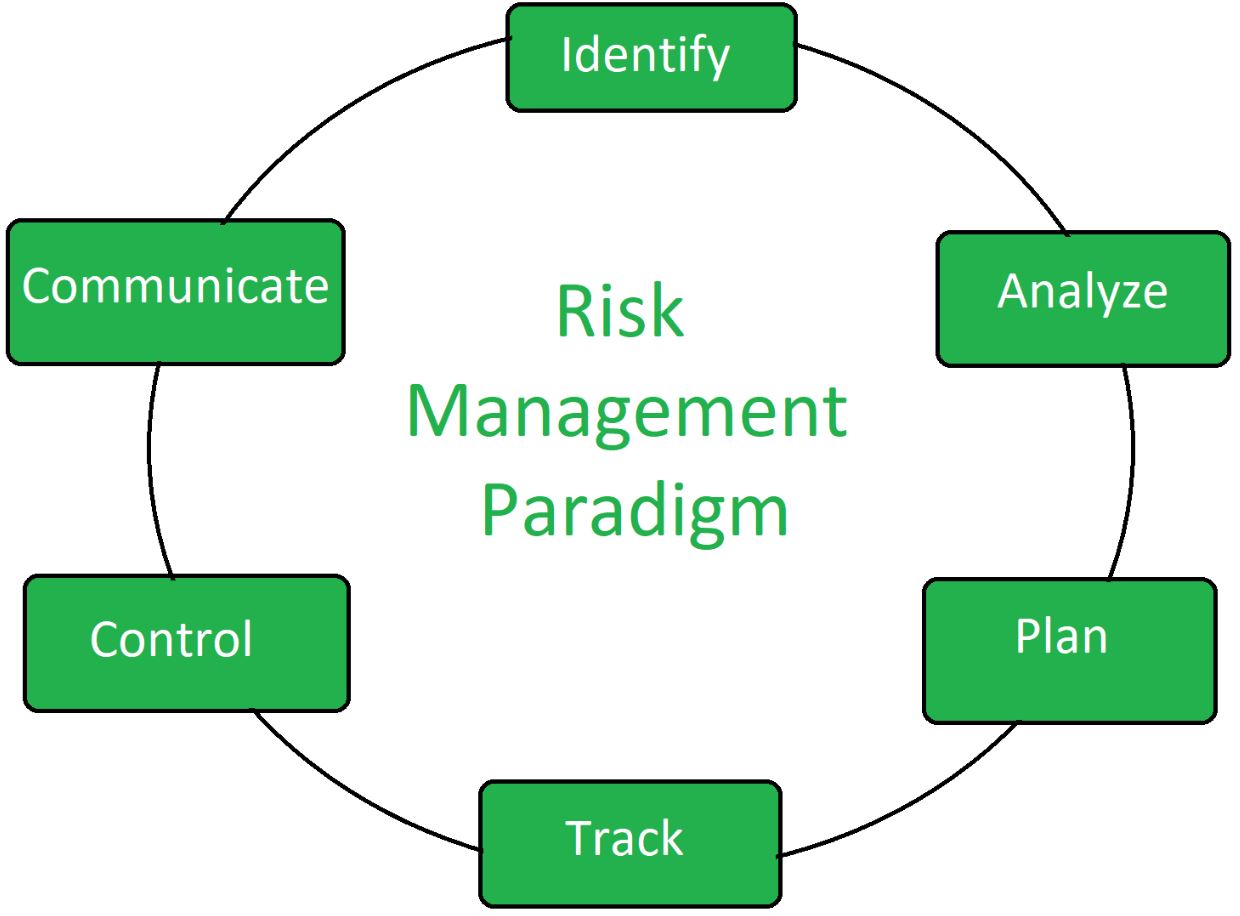
Risk Management Process:
- Context Establishment: Define the organizational context for risk management.
- Risk Identification: Identify potential risks.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the risks in terms of impact and likelihood.
- Risk Treatment: Develop and implement strategies to manage or mitigate risks.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously monitor and review the effectiveness of risk management strategies.
- Strategic Objectives: Define high-level organizational goals.
- Resilience Policy: Establish policies to enhance organizational resilience.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics to measure the effectiveness of resilience efforts.
- Action Plans: Specific steps and initiatives to implement resilience policies.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources to support resilience initiatives.
-
Planning and Direction:
- Define intelligence requirements and objectives.
-
Collection:
- Gather relevant information from various sources.
-
Processing:
- Organize and analyze collected data to extract meaningful intelligence.
-
Analysis and Production:
- Evaluate and interpret processed information to generate intelligence.
-
Dissemination:
- Share intelligence with relevant stakeholders.
-
Feedback:
- Gather feedback to improve the intelligence cycle.
-
Identification:
- Recognize and clarify the issue or problem.
-
Research:
- Gather relevant information and perspectives.
-
Analysis:
- Evaluate information, identify patterns, and assess implications.
-
Generating Alternatives:
- Propose various solutions or approaches.
-
Decision Making:
- Select the best course of action based on analysis.
-
Implementation:
- Put the decision or solution into action.
-
Evaluation:
- Assess the outcomes and adjust strategies if needed.